1. Introduction to Light Poles
Light poles are ubiquitous elements in urban landscapes, serving as essential components of public infrastructure. They are vertical structures designed to support lighting fixtures, providing illumination for streets, parking lots, and various outdoor spaces. The primary purpose of light poles is to enhance visibility and safety during nighttime or low-light conditions. By illuminating pathways, intersections, and public areas, light poles play a crucial role in urban planning, contributing to the safety and security of pedestrians and drivers alike.
In addition to their functional role, light poles also contribute to the aesthetic appeal of urban environments. They can be designed to complement architectural styles and enhance the visual landscape of cities. As such, light poles are integral to both the practical and aesthetic aspects of urban planning.
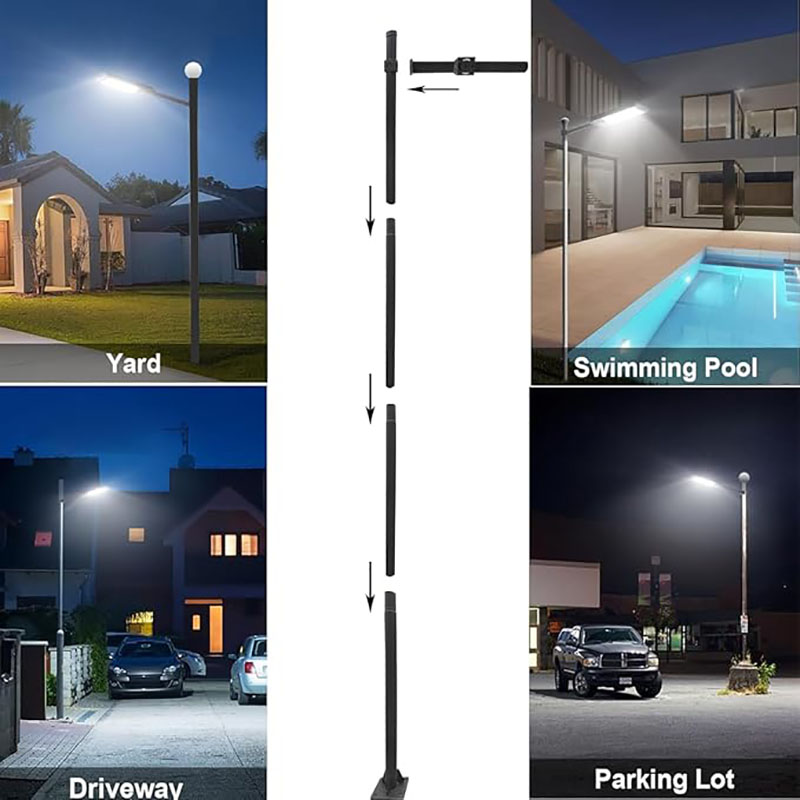
2. Types of Light Poles
Light poles are manufactured from various materials, each offering distinct advantages and characteristics. The choice of material often depends on factors such as durability, cost, and environmental considerations.
- Steel Light Poles: Steel is a popular choice for light poles due to its strength and durability. Steel poles are capable of withstanding harsh weather conditions and are often used in areas prone to high winds or heavy traffic. They are typically coated with protective finishes to prevent corrosion and extend their lifespan.
- Aluminum Light Poles: Aluminum poles are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for coastal areas or regions with high humidity. They are easier to install and transport compared to steel poles, and their natural resistance to rust reduces maintenance requirements.
- Fiberglass Light Poles: Fiberglass poles are known for their flexibility and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and UV radiation. They are non-conductive, making them a safe option for areas prone to electrical storms. Fiberglass poles are also lightweight, which simplifies installation.
- Decorative Light Poles: These poles are designed with aesthetics in mind, often featuring intricate designs and finishes that enhance the visual appeal of public spaces. Decorative poles are commonly used in historic districts, parks, and pedestrian areas where visual impact is a priority.

3. Applications of Light Poles
Light poles are versatile structures used in a variety of settings to provide illumination and enhance safety.
- L'éclairage des rues: One of the most common applications of light poles is street lighting. Properly illuminated streets improve visibility for drivers and pedestrians, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing public safety.
- Places de parking: Light poles are essential in parking lots, where they provide the necessary illumination for vehicle and pedestrian movement. Adequate lighting in parking areas deters criminal activity and ensures the safety of users.
- Outdoor Spaces: Light poles are also used in parks, gardens, and recreational areas to create inviting and safe environments. They enhance the usability of outdoor spaces during evening hours, encouraging community engagement and outdoor activities.
4. Material Considerations
When selecting light poles, several material considerations come into play, influencing the decision-making process.
- Durability and Maintenance: The durability of light poles is a critical factor, especially in areas with extreme weather conditions. Materials like steel and aluminum offer high durability, while fiberglass provides excellent resistance to environmental factors. Maintenance requirements vary depending on the material, with some requiring regular inspections and protective coatings.
- Cost Implications: The cost of light poles varies based on the material and design. Steel poles are generally more expensive due to their strength and durability, while aluminum and fiberglass poles offer cost-effective alternatives with lower maintenance costs.
- Impact environnemental: The environmental impact of light poles is an important consideration, particularly in sustainable urban planning. Aluminum and fiberglass poles are often preferred for their recyclability and lower environmental footprint compared to steel.

5. Technological Advancements
The evolution of technology has significantly impacted the design and functionality of light poles, leading to innovative solutions that enhance their efficiency and utility.
- Integration with LED Lighting: The integration of LED lighting technology with light poles has revolutionized outdoor illumination. LED lights are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and provide superior illumination compared to traditional lighting options. This integration reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs, making it a sustainable choice for urban lighting.
- Smart Pole Technology: Smart poles represent the future of urban lighting, incorporating advanced technologies such as sensors, cameras, and wireless communication. These poles can monitor environmental conditions, manage traffic flow, and provide real-time data to city planners. Smart poles enhance urban infrastructure by offering multifunctional capabilities beyond traditional lighting.
6. Conclusion
In summary, light poles are indispensable elements of urban infrastructure, providing essential illumination for safety and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of public spaces. The choice of material, whether steel, aluminum, or fiberglass, depends on factors such as durability, cost, and environmental impact. Technological advancements, particularly the integration of LED lighting and smart pole technology, are shaping the future of light poles, offering innovative solutions for sustainable urban development.
As cities continue to grow and evolve, the role of light poles in urban planning will become increasingly important. Future trends may include further advancements in smart technology, increased focus on sustainability, and the development of new materials that offer enhanced performance and reduced environmental impact. Light poles will remain a vital component of urban landscapes, illuminating the way forward for safer and more connected communities.